Projects
Topology Adaptation for Robust Networks
Wireless networks are easily susceptible to a variety of attacks due to its transmission via an open medium which allows observation and introduction of interference and false messages. These problems are particularly pernicious in the case of ad hoc networks, where nodes in the network inter-communicate with each other in a dynamic and opportunistic manner. A node in an ad hoc network can either be a router or a terminal node. A malicious attacker can simply launch a powerful interference to cause its surrounding legitimate nodes to shut down and disable its ability to notify other nodes. For an instance, jamming attack can easily happen through a single specialized chip or a cell phone. As a counter-measure, I have proposed an algorithm to strengthen the reliability of transmission when jammer shuts down one or several legitimate nodes in ad hoc networks.
- Ying Liu, Wade Trappe, "Jammer Forensics: Localization in Peer to Peer Networks Based on Q-learning", the 40th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2015), Brisbane, Australia, April 2015, to appear
Game Theory for Modeling Security Problems in Ad Hoc Networks
Game Theory is a natural tool to model the rational behaviors between legitimate users and jammers in Ad Hoc networks. It examines the interactions between players to derive Nash Equilibrium strategies for them when players have either obtained complete or incomplete information. Many network security problems can be described as a zero-sum game between two players and cooperation games among a group of players. For example, at the physical layer, jamming and eavesdropping attacks happen frequently and the behavior of jamming attacks can be modeled as simultaneous games where both the legitimate user and jammer want to achieve their specific goals without knowing the exact channel conditions of the opponent. Whereas, the eavesdropping attack is modeled as Stackelberg game which the legitimate user transmits signal first and the eavesdropper takes corresponding actions in order to intercept the signal and to gather as much information as possible.
- Andrey Garnaev, Ying Liu, Wade Trappe, "A Low Power Jamming Attack against a P2P Wireless Network", IEEE Communications Letters, submitted
- Andrey Garnaev, Ying Liu, Wade Trappe,"An Anti-jamming Strategy for a Coalition Versus a Team of Jammers in a P2P Network", Ad Hoc Networks, submitted
Scalable MANET-based Peer-to-Peer VoIP/Multimedia Architecture (finished)
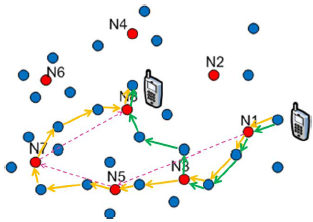 Overlay networks is a beneficial approach to designing robust and specialized networks on top of the generic IP architecture, and this concept have been applied to the operation of mesh and mobile ad hoc networks. Unfortunately, when routing between entities in the overlay, inefficiencies are incurred due to potential "back tracking" that arises because of the discrepancies between the overlay and underlay topologies. In my research, I minimize the “back tracking” problem by applying physical contexts shared by the network layer with the overlay so it can efficiently guide application flow. I have devised an intelligent cluster head and path selection algorithm for overlay routing and successfully compared its superior performances with the popular Chord protocol and a baseline AODV routing protocol.
Overlay networks is a beneficial approach to designing robust and specialized networks on top of the generic IP architecture, and this concept have been applied to the operation of mesh and mobile ad hoc networks. Unfortunately, when routing between entities in the overlay, inefficiencies are incurred due to potential "back tracking" that arises because of the discrepancies between the overlay and underlay topologies. In my research, I minimize the “back tracking” problem by applying physical contexts shared by the network layer with the overlay so it can efficiently guide application flow. I have devised an intelligent cluster head and path selection algorithm for overlay routing and successfully compared its superior performances with the popular Chord protocol and a baseline AODV routing protocol.
- Ying Liu, Xiruo Liu, Wade Trappe, Radhika Roy, "Distance-aware Overlay Routing with AODV in Large Scale Ad Hoc Networks", IEEE 80th Vehicular Technology Conference, Vancouver, Canada, Sept., 2014